Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism, also known as underactive thyroid, is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It causes a number of symptoms, such as the poor capacity to tolerate cold, a feeling of lassitude(tiredness), depression, constipation, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated hypothyroidism during pregnancy may lead to delays in growth and intelligent development in the baby, which is called cretinism.

You Might Also Like:
- Eczema :Symptom,Causes,Medication & Ointment
- Gout Arthritis: Symptom, Causes, Treatment & Gout Diet
- What is Physical Therapy? Role & Benefits of Physiotherapy
- PITUITARY GLAND: PARTS, LOCATION & FUNCTION
Symptoms of an Underactive Thyroid
Many symptoms of hypothyroidism are the same as those of other conditions, so it confused for something else.
Symptoms may usually develop slowly and may not realize you have a medical problem for several years.
Common symptoms include:
- Tiredness
- Poor capacity to tolerate cold
- Weight gain
- Depression
- Constipation
- Muscle pain and weakness
- Muscle cramps
- Dry and scaly skin
- Brittle hair and nails
- Loss of libido (sex drive)
- Numbness, Pain and also the tingling sensation in the hand and fingers (Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)
- Irregular periods
Elderly people with hypothyroidism may develop memory problems with depression. Children can experience slower growth. In the case of teenagers may start puberty earlier than normal.
If an underactive thyroid isn’t treated Later symptoms of an underactive thyroid include:
- Hoarse voice and a low-pitched and
- Puffy-looking face
- Partly missing eyebrows
- Loss of hair
- Anemia
- Slow heart rate
Causes of underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
An underactive thyroid is when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroxine hormone (known as T4).
Most cases hypothyroidism is caused by the immune system attacking the thyroid gland and damaging it.
Immune system
Hypothyroidism occurs when the immune system, which usually fights infection, attacks the thyroid gland. This damages the thyroid gland, and it’s not able to make enough thyroxine hormone.
Previous thyroid treatment
An underactive thyroid may occur as a complication of previous treatment to the thyroid gland, such as a treatment of radioactive iodine therapy.
These treatments are sometimes used for an overactive thyroid or thyroid cancer.
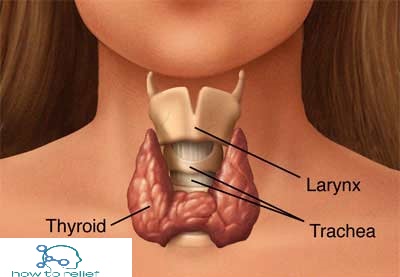
Less common causes
- Lack of dietary iodine a common cause of hypothyroidism, because the body needs iodine to make the thyroxine hormone.
- Babies are sometimes born with an underactive thyroid because thyroid gland doesn’t develop properly in the womb.
- The pituitary gland situated at the base of the brain and regulates thyroid hormone. A problem with pituitary gland can lead to hypothyroidism or an underactive thyroid.
- Hypothyroidism has also been linked to some viral infections or medications used to treat other conditions, such as:
lithium – a medication used to treat certain health conditions, including depression and bipolar disorder
amiodarone – a medication used to treat irregular heartbeats
interferons – a medication used to treat cancer and hepatitis C
Diagnosis of Underactive Thyroid

Thyroid function test
- A blood test measuring the thyroid hormone levels is an accurate way to find out hypothyroidism.
- The test of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) in the blood.
- A high level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and a low level of T4 in blood could mean have an underactive thyroid.
- If the test results show raised TSH but normal T4, you may have the risk of developing an underactive thyroid in the future.
Your physicians may recommend a repeat blood test every so often to see whether to eventually develop an underactive thyroid.
Treatment of Underactive Thyroid
Hypothyroidism is commonly treated by taking daily hormone replacement tablets( levothyroxine). You may initially have regular blood tests until the correct dose of levothyroxine is reached.
You may initially start on a low dose of levothyroxine, that may be increased gradually, depending on how the body responds.
Hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid is a lifelong condition, so you may need to take levothyroxine for the rest of life.
Possible Side effects
Levothyroxine doesn’t have any side effects because the tablets simply replace missing hormone thyroxine.
Side effects only occur if taking too much levothyroxine. This may cause sweating, chest pain, headaches, diarrhea, and vomiting.

