Diabetes Mellitus: An estimation Americans have 26 million diabetes patient, a disease in which there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. About 7 million of them, however, have not yet been diagnosed with the Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes occurs when the pancreas, a gland abaft the stomach, does not engender enough of the hormone insulin or the body can’t use insulin felicitously. Insulin avails carry sugar from the bloodstream into the cells. Once sugar is converted into energy inside the cells for immediate use or stored for the future. That energy fuel makes our body functions.

Types of Diabetes
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Diabetes During Pregnancy
Type 1 Diabetes– Occurs when the pancreas makes very little or no insulin. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin every day to supersede the insulin their bodies are not making. This form of the disease is most often visually perceived in children. It used to be called or juvenile diabetes, but it can occur at any age.
Type 2 Diabetes– Is the most prevalent form of the disease, affecting 90 to 95 percent of people with diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, the body is resistant to the action of insulin(insulin resistance), betokening it cannot use insulin opportunely, so it cannot carry sugar into the cells. Albeit the body makes some insulin, it is not enough to surmount this resistance. You are more liable to develop diabetes if you are inordinately corpulent, have a family history of diabetes, or have a history of diabetes during gravidity. Other groups more liable to have the disease are people over age 46 and non-Caucasians. A simple blood sugar test can tell you if you have diabetes.
Diabetes During Pregnancy– A transitory form of diabetes can occur when a woman is pregnant. This is gestational diabetes and often has no sign of sickness. Most women are got high blood sugar during their pregnancy. If a woman has high blood sugar level, she will have must follow a special diet for the rest of the pregnancy period. In some cases, she may additionally need to take insulin. About 3 to 5 percent of pregnant women develop gestational diabetes.
Symptom of Diabetes
People can experience different signs and symptoms of diabetes, and sometimes there may be no designations. Some common sign & symptom individual experienced include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent micturition
- Incremented hunger
- More tired than usual
- Losing weight with-out try
- Apathy and concentration
- Tingling feeling or numbness in the hands or feet
- Blurred vision
- Intermittent infection
- Wounds take longer to heal
- Regurgitating and stomach pain
The development of type 1 diabetes is usually sudden and dramatic while the symptoms can often be mild or absent in people with type 2 diabetes, making this type of diabetes hard to detect.
Don’t ignore these signs and symptoms if you have, engender Ment talk to a health professional.
Causes of Diabetes
Affecting an estimated 26 million Americans, diabetes is a fairly prevalent condition relating to quandaries engendered that has two forms: type 1 and type 2. While the exact causes of diabetes have not been determined, some risk factors have been identified as being cognate to the condition.
You Might Also Like:
- Glucometers: Types, Buying Guide & Popular Glucometers Brands
- EKG/ECG Machines: Popular Brand EKG Machine
- Glaucoma: Symptoms, Types, Causes & Treatment
- Diabetes Diet: What to Eat & Avoid
Risk Factors of Diabetes

For type 1 diabetes, the body ceases making insulin because its immune system has commenced assailing and ravaging the cells where insulin is made — this form of the disease influenced by environmental factors, genetics and potentially even exposure to certain viruses.
For type 2 diabetes, where the body either isn’t making enough insulin or isn’t utilizing its insulin as efficiently as it could, genetics, lifestyle factors, extravagant corpulence, and a lethargic lifestyle are typically involved. While the sign of sickness is typically the first warning signs that patients noticed, a simple fasting & random blood test will be able to reveal whether or not someone has the exact condition.
Diabetes Treatment & Care

Diabetes is a prevalent disease, every individual needs unique care. We embolden people with diabetes and their families to learn as much as possible about the latest medical approaches, as well as the salubrious lifestyle. Good communication with a team of experts can avail you feel in control and respond to transmuting needs.
The major goal of treating diabetes is to control blood sugar levels within the normal range.
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment:
- Insulin,
- Exercise, and a
- Type 1 diabetes diet.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment:
- Weight reduction,
- Type 2 diabetes diet, and exercise
- Oral medications are prescribed when these quantifications fail to control the elevated blood sugars of type 2 diabetes.
If oral medications become fail to treatment then insulin is initiated.
Complication of Diabetes
People with diabetes have an incremented risk of developing a number of earnest health problem. Consistently high blood glucose levels can lead to solemn diseases affecting the heart and blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and teeth. People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing infections. In virtually all high-income countries, diabetes is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, visual impairment, kidney failure, and lower-limb amputation.
Maintaining blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol at or proximate to mundane can avail delay or obviate diabetes complications. Consequently, people with diabetes need conventional monitoring.
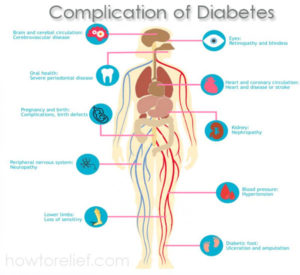
Cardiovascular Disease- affects the heart and blood vessels and may cause deadly difficulties such as coronary artery disease (leading to heart attack) and stroke. Cardiovascular disease is the most mundane cause of death in people with diabetes. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, high blood glucose, and other risk factors contribute to incrementing the peril of cardiovascular complications.
Kidney Disease (Diabetic Nephropathy)- caused by damage to diminutive blood vessels in the kidneys leading to the kidneys become less efficient or to fail altogether. Kidney disease is much more prevalent in people with diabetes than in those without diabetes. Maintaining near mundane levels of blood glucose and blood pressure can greatly reduce the peril of kidney disease.
Nerve Disease (Diabetes Neuropathy)- High blood sugar level & blood pressure can cause damage to the nerves throughout the body. This can lead to quandaries with digestion, erectile dysfunction, and many other functions. Nerve damage in these areas is called peripheral neuropathy and can lead to pain, tingling, and loss of feeling. Loss of feeling is categorically paramount because it can sanction injuries to go unnoticed, leading to earnest infections and possible amputations. People with diabetes carry a peril of amputation that may be more than 25 times more preponderant than that of people without diabetes. However, with comprehensive management, an astronomically immense proportion of amputations cognate to diabetes can be obviated. Even when amputation takes place, the remaining leg and the person’s life can be preserved by good follow-up care from a multidisciplinary foot team. People with diabetes should customarily examine their feet.
Eye Disease (Diabetic Retinopathy)- Most people with diabetes will develop some form of ocular perceiver disease (retinopathy) causing reduced vision or optical incapacitation. Consistently high calibers of blood glucose, together with high blood pressure and high cholesterol, are the main causes of retinopathy. It can be managed through conventional ocular perceiver checks and keep glucose and lipid levels at or proximate to normal.
Pregnancy Difficulties- Women with any type of blood sugar swings during pregnancy risk some difficulties if they do not punctiliously monitor and manage their condition. To prevent possible organ damage to the unborn baby, women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes should maintain target blood sugar levels before conception. All women with diabetes should work hard to target blood sugar levels to minimize complication.
High blood glucose during pregnancy can lead to excess weight to the fetus. This can lead to puzzling and difficult situations in delivery, serious physical harm to the child and mother, and a sudden drop in blood glucose for the child after birth. A fetus who is high blood glucose in the womb is the higher risk of developing diabetes in the future.
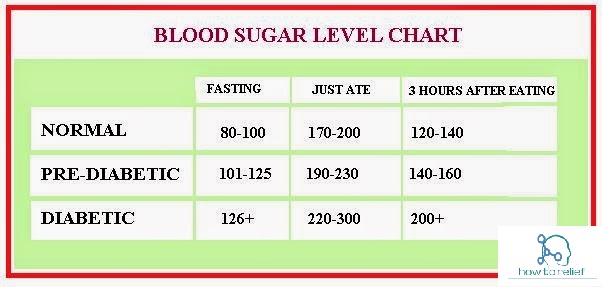
Normal Blood Sugar Level(Adult)